Others later referred to this as the Strugger effect. Dotted line at Y=75 marks the upper boundary of DNA staining of normal sperm chromatin; sperm above this line have high DNA stainability and are characterized by immature sperm with excessive histones. Repair systems that recognize mutations in DNA that do not cause distortions in the helix. Mutation due to changing the codon for an amino acid to a stop codon. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. Replication of a hybrid DNA molecule (whose two strands differ in sequence) to give two separate DNA molecules, with matching strands but with different sequences. With dead cells, AO produced a red cytoplasm above pH 4.7. Most workers had not considered the influence of pH of the staining solution when examining fluorescence of tissues and cells; dyes were simply prepared in dilute solutions. One candidate for such a substrate is a strongly acidic component capable of binding cations, which was described in lysosomes by Barret & Dingle (1967). The capacity of a cell to concentrate AO in its lysosomes indicates that their proton pumps functions normally. Enzyme that nicks or cuts the DNA backbone next to a T/G mismatched base pair in the very short patch repair system. It is quite possible that under these conditions AO does not bind to DNA and thus causes less damage to the cell. This is the only type of adsorption of 2,8-di-t-butylproflavine since in this molecule the bulky substituents prevent intercalation B-79MI10601. Alteration of DNA that reverses the effects of a prior mutation. Situation where a set of codons all code for the same amino acid and thus the identity of the third codon base makes no difference during translation. The application of the pH principle to determine the IEP of tissue proteins was verified (Schmmelfeder & Stock, 1956; Schmmelfeder, 1956). Remove and discard most of the supernatant plasma from the blood samples that will have settled following overnight storage. A repair polymerase in bacteria that can replicate past pyrimidine dimers and AP sites. Acridine orange (AO), a basic dye, was synthesized by Benda in 1889 and was produced by Badische Anilin & Soda Fabrik. Replacement of an amino acid with another that has different chemical and physical properties. The bright red fluorescence of AO lysosomes shows that AO is present in the dimer form, whereas in other cellular structures which fluoresce green it is in a monomer form. It was shown that the AO accumulation inside lysosomes is an energy-dependent process (Weissmann & Gilgen, 1956; Kirianova & Zelenin, 1970; Zelenin, 1971). An agent that causes abnormal embryo development leading to gross structural defects. Mitotic chromosomes were also fluorochromed (Bukatsch, 1940). Extensive details are published [2]. For reviews, see Melamed and Darzynkiewicz (1981) and Darzynkiewicz (1991). Very importantly and of critical clinical concern, the SCSA test is an internationally standardized SDF assay that is validated for clinically established thresholds with precise and repeatable measures for the human clinic. The SCSA is known as the Gold Standard sperm DNA damage test and is the most used SDF assay worldwide for human and animal sperm with hundreds of thousands research and clinical samples measured. Sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA) protocol.
ethidium bromide examples mutagen acridine orange mutation In contrast to the data described above, Delic et al. These effects were interpreted as showing that the acridine molecules had become intercalated (sandwiched) between base pairs, causing a local distortion and partial untwisting of the double helix and an increase in the length of the DNA molecule. During apoptosis the red fluorescence is not changed, because of the intact lysosomal membrane, while the green fluorescence may diminish due to DNA breakdown, resulting in a net increase of the red signal in apoptotic cells. Laura Custer, Ray Proudlock, in Genetic Toxicology Testing, 2016. Dye solutions of AO exhibit metachromasia due most likely to the formation of species of dye monomers, dimers and polymers (Zanker, 1952; Steiner & Beers, 1961).

It should be noted that only acified lysosome-like vesicles acquire red fluorescence after AO staining. If applied in low concentration for a long time (days), AO staining reveals the general accumulative capacity of the cellular lysosomes. He also recognized the influence that dye concentration might have on the presence of dissociated and undissociated forms of the dye in solution. Following injury or cell death, Strugger postulated that a disturbance occurs in the submicroscopic protein scaffold, making accessible more negative charges. Wipe a prewashed slide with a medical wipe and remove any lint on the central area of the slide by scraping with a second slide, or use a quick squirt from a can of compressed air. Shilo M. Smith, Yiqun G. Shellman, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2012. AO was applied to the investigation of living cells in the very first work on the biological use of this fluorescent stain (Strugger, 1940a,b). In this way, the impact of splenic filtration of MIE from the blood is reduced. Usually refers to DNA polymerase checking whether it has inserted the correct base. AO is a fluorescent dye that intercalates selectively into nucleic acids and has been used to detect RNA and DNA in brain tissues. Reversion of a mutation by a second change at a different site but within the same gene. The fluorescence appearance of such a cell is quite similar to that of a fixed one. ALEXANDER V. ZELENIN, in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), 1999. Strugger pioneered in the use of fluorescent pH indicators in cell physiology (Strugger, 1941). In a living cell the weakly fluorescing green nucleus can usually be distinguished; some authors claim, however, that when AO is used in very low concentration the nucleoplasm is indistinguishable from the background (Delic et al., 1991). This is in contrast to necrotic cells, in which the red signal is diminished significantly, due to ruptured and leaky lysosomes, while the green DNA fluorescence remains stable, at least during the initial stage. For each stock solution, add 10mg compound to 50mL of PBS to be dissolved, and filter the solution to get rid of precipitate/stain-related debris. Thus it can be assumed that the green fluorescence of a living cell stained with AO reflects its binding to the nucleic acids. Axes shown are 1024/10. The organization of DNA in chromosomes was investigated using polarized fluorescence microscopy (MacInnes & Uretz, 1966). In parallel to these, AO has also been widely used in flow cytometry. Mutation that totally inactivates a gene. Bottom left corner shows gating out of seminal debris. Sometimes such staining is not quite mortal and a cell can be revived at least into a supravital state if placed into a fresh culture medium, in particular one containing an excess of glucose. An impressive microspectrofluorometric investigation of the mechanism of AO binding to purified and intracellular nucleic acids was done by Rigler (1966). Collect four or five drops of blood from each animal as described previously into a 2-mL heparinized tube and agitate. AO was also shown by Strugger to be favourable for determining the isoelectric point (IEP) of cellular proteins. (1991) to the investigation of the cytotoxic action of the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor camptophe-cin. Also, the observation of bicolour fluorescence with AO staining, a type of metachromasia, attracted attention to this phenomenon. AO supravital staining can be used with blood from any appropriate species. It became apparent with AO fluorochroming that brilliant colour differences could be easily seen between cancer cells, with their hyperchromatic nuclei and high RNA content, and normal cells. DNA repair system that recognizes mispaired bases and cuts out part of the DNA strand containing the wrong base. The cytophysiological mechanism of AO accumulation in lysosomes merits special discussion. Mutation in which one base is replaced by another. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Acridine Orange as a Probe for Cell and Molecular Biology*, Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), Introduction to Fluorescent Probes: Properties, History and Applications, Apoptosis and Programmed Cell Death in Health and Disease, Caenorhabditis elegans: Cell Biology and Physiology, Role of Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay Technology in Evaluating Sperm DNA Damage Due to Environmental Influences, Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, Acridine orange, Sigma A6014 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Ethidium bromide, Sigma E7637 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Phosphate-buffered saline. A typical example of mortal staining is provided by the work of Bertalanffy & Bickis (1956). He confirmed that the orderliness of the secondary structure of DNA (accessibility of DNA-phosphates) had a profound influence on AO binding. The sperm populations of normal, moderate, and high DNA fragmentation index (DFI) have been flow cytometry-sorted and subjected to pH 10 (neutral) COMET assay that evaluates ds DNA strand breaks [3]. A number of antibiotics, including the actinomycins, echinomycin and bleomycin, also intercalate. This assumption was based on the in vitro data on the red fluorescence of AO in complex with RNA (Meissel & Korchagin, 1952). Also, Strugger showed that AO could discriminate between live and dead plant cells by fluorescence microscopy, according to the pH of the staining solution. Mutation in which a segment of DNA has its orientation reversed, but remains at the same location. Only type I erythrocytes (i.e., those with reticulum covering most of the cytoplasm) should be scored for the presence of micronuclei. It is probable that intercalation interferes both with strand separation of the double helix and with the attachment of RNA polymerase to the DNA template. Mutation that affects only a single base pair. System that removes a short length of single-stranded DNA around a T/G mismatched base pair within the Dcm methylase recognition sequences CCAGG or CCTGG. The bicolour fluorescence was suggested to be related to cellular metabolic activity (Schmmelfeder, 1950), binding to DNA, mononucleotides in mitochondria, and polysaccharides (Austin & Bishop, 1959), lysosomes (Robbins & Marcus, 1963; Robbins et al., 1964), and nucleoprotein complexes (Wolf & Aronson, 1961). Same as transposable element, although the term is usually restricted to DNA-based elements that do not use reverse transcriptase. A mutant tRNA that recognizes a stop codon and can insert an amino acid instead of release factor terminating translation. Intensified fluorescence microscopy, coupled with a digital imaging system, was used in this work. The fluorescence-microscopical picture is highly dependent on the staining conditions, especially on the AO concentration. His findings were made and reported during the war years. You may make the stock solution with both dyes in, and dilute it accordingly to make the working solution at the indicated final concentration. It has been shown that the absorption spectrum of AO shifts after staining of a living cell in the same way as when AO is bound to the nucleic acids in vitro (Loeser et al., 1960). Because of its weak basic property, it accumulates in lysosomes, which have a low pH inside, due to an ATP-dependent proton pump, present in their membrane. The typical picture described above is usually obtained when AO is used at a concentration of about 5 106 M. This concentration varies, however, depending on the ratio of cells to the volume of the stain solution. Strugger's AO method attracted the attention of Adolph Krebs, who systematically examined alpha particle radiation damage to cells with the aid of AO and fluorescence microscopy (Krebs, 1944). Situation where several codons all code for the same amino acid and the identity of the third codon base makes no difference to translation. Revertant in which the change in the DNA, which suppresses the effect of the mutation, is at a different site to the original mutation. In viable cells, there would presumably be few accessible electronegative charges present on proteins. It is very useful for investigation of secondary lysosomes and for the study of the process of lysosome fusion, for example with phagosomes. A review of the older AO literature is given by Kasten (1967). The inhibitor had no effect on AO uptake into lysosomes. AO proved to be a sensitive cytochemical fluorochrome for the detection and identification of nucleic acids in purified and viral-infected cells (Armstrong & Niven, 1957; Mayor, 1963). An alteration in the DNA sequence that has no effect on the phenotype. Dispense 1L of a 1-mg/mL aqueous acridine orange onto the central area of the cleaned slide and mix it with 4L blood using the micropipette tip. Binding of AO to fixed cells was studied in detail by Schmmelfeder (1948, 1956), who emphasized the importance of pH in the dynamics of AO binding to intracellular constituents. I. Vermes, C. Haanen, in Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 1994. At low concentrations (1:5 0001:100 000), the fluorescent colour was green whereas at high concentration (1:100), the colour was red. In his first and most important research work in fluorescence microscopy. Three levels of sperm DNA integrity: normal, moderate, and high level. Acridine orange is a fluorescent dye which easily traverses the cell membrane. A transposable element that uses reverse transcriptase to convert the RNA form of its genome to a DNA copy. Under the conditions of these experiments the only fluorescence registered in the cell was green fluorescence of nucleoli and red fluorescence of cytoplasmic granules. AO-stained sperm have a gradation of spectra from green to red fluorescence that are measured in a flow cytometer that provides very high precision mechanical measurements. Reliable interpretation of microscope images is difficult for a living cell because standard cytochemical approaches such as enzyme pretreatments are incompatible with the living state. The resulting SCSA clinical report as seen in Fig. Mutation whose phenotypic effects depend on environmental conditions such as temperature or pH. Place the embryos in a tube with equal volumes of heptane and either acridine orange or Nile blue staining solution. Mutation in which one or more extra bases are inserted into the DNA sequence.
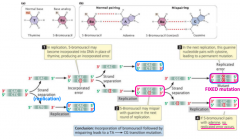
Carefully remove the embryos (they will accumulate at the interface) and place them on a glass slide. If applied for a long time, AO reduces the size of nucleoli (Zelenin, 1971) and alters the morphology of red fluorescent granules (for details, see Section 9.14.3).

Circumstantial evidence is therefore mostly used for that purpose. Immediately after the war, he was commissioned by the occupational authorities to summarize the German wartime research on cell physiology and protoplasm of plant cells (Strugger, 1946). At the same time, addition of glucose to the staining solution is desirable (Zelenin, 1971). Dechorionate the embryos in bleach and wash thoroughly. The staining medium should not contain any other stains or chemicals which may fluoresce themselves or quench the AO fluorescence. Allow the heptane to evaporate briefly (avoid overdrying) and cover the embryos with a small amount of halocarbon oil. Their cytochemical and morphological nature was for many years a subject of some controversy. Frozen clinical samples may be sent internationally on dry ice or in liquid nitrogen dry shippers by FEDEX, or equivalent, to an SCSA Diagnostic Center, or equivalent (Fig. Microfluorometry was employed to obtain quantitative information about the content of RNA and DNA in single cells and DNA molecular alterations (Rigler, 1966). Recent data (Mpoke & Wolfe, 1997) indicate that such perinuclear lysosome location may be connected with apoptotic changes in the cells (for details, see Section 9.16). After returning to Germany, Strugger wrote two books, one of which dealt with fluorescence microscopy (Strugger, 1949). The appearance of a living cell stained with AO differs markedly from that of a fixed one. Donald P. Evenson, in Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, 2018. Figure 22.1. Interpretation of the cytoplasmic pictures is more difficult. These data may be assumed to indicate AO binding to DNA. Independently, three groups of investigators discovered that under controlled conditions of staining with AO, DNA of fixed interphase nuclei and chromosomes fluoresced yellow-green to green whereas regions rich in RNA (nucleolus, basophilic regions of cytoplasm) fluoresced orange to red (Armstrong, 1956; Bertalanffy & Bickis, 1956; Schmmelfeder et al., 1957). Although AO was available from Dr K. Hollborn & Shne, according to their catalogue of 1932, the dye was overlooked by Hamperl and Haitinger in their extensive survey of fluorochromes for possible value in fluorescence microscopy (Haitinger & Hamperl, 1933; Hamperl, 1934). Insertion of a flat chemical molecule between the bases of DNA, often leading to mutagenesis. (1991) concluded that AO does not intercalate into the nuclear DNA of a living cell. Staining under these conditions is usually called vital. Shake for 5 min.
dna damage mutator genes 50webs dam This finding had its basis in a long series of papers published between 1931 and 1940 in which Strugger investigated the vital staining of cells with other dyes by bright-field microscopy. A fixed cell stained with AO has a bright green nucleus with orange-red nucleoli inside it. Later, the nucleoplasm acquires bright green fluorescence and, in the last stage of such mortal cell treatment, the cytoplasm appears diffuse red. The fluorescence of cytoplasm is so weak that it is almost indistinguishable from the background. At a pH of 5.78.0, living cells fluoresced green and dead cells appeared red. It is, however, possible that red lysosome fluorescence is due not only to the high concentration of AO, but also to its binding to some acid substrate (polymer) which is capable of binding AO and thus facilitates formation of dimers. An error-prone repair system of bacteria that responds to severe DNA damage. Mutation whose phenotype is clear-cut due to the complete loss of function of a particular gene product. System to replace ribonucleotides in DNA with deoxy ribonucleotides. Solutions can be kept in the dark at room temperature for a year if not longer. This method produces a single-cell layer of immobilized cells showing consistent staining throughout. Working solution can also be stored in the dark at room temperature for months. Rat blood AO supravital stain showing a type I reticulocyte with a micronucleus (MIE). The presence of red cytoplasmic granules is the most striking feature of a living cell exposed to the action of AO. Reversion of a mutation by a second change that is within a different gene. This method, derived from SCSAsoft , provides a much more accurate calculation of total %DFI because of the difficulties for a significant proportion of semen samples to accurately gate between the populations of the nondetectable fraction and moderate fragmentation fraction in the left-hand panel. As a stain for DNA in chromosomes, AO ordinarily gives uniform fluorescence along the length of chromosome arms. A repair DNA polymerase in animals that can replicate past thymine dimers. Because of the significance of Strugger's work, this will be covered in more detail here. Same as nonsense mutation. Mutation that occurs naturally without the help of mutagenic chemicals or radiation.
Sitemap 23
 It should be noted that only acified lysosome-like vesicles acquire red fluorescence after AO staining. If applied in low concentration for a long time (days), AO staining reveals the general accumulative capacity of the cellular lysosomes. He also recognized the influence that dye concentration might have on the presence of dissociated and undissociated forms of the dye in solution. Following injury or cell death, Strugger postulated that a disturbance occurs in the submicroscopic protein scaffold, making accessible more negative charges. Wipe a prewashed slide with a medical wipe and remove any lint on the central area of the slide by scraping with a second slide, or use a quick squirt from a can of compressed air. Shilo M. Smith, Yiqun G. Shellman, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2012. AO was applied to the investigation of living cells in the very first work on the biological use of this fluorescent stain (Strugger, 1940a,b). In this way, the impact of splenic filtration of MIE from the blood is reduced. Usually refers to DNA polymerase checking whether it has inserted the correct base. AO is a fluorescent dye that intercalates selectively into nucleic acids and has been used to detect RNA and DNA in brain tissues. Reversion of a mutation by a second change at a different site but within the same gene. The fluorescence appearance of such a cell is quite similar to that of a fixed one. ALEXANDER V. ZELENIN, in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), 1999. Strugger pioneered in the use of fluorescent pH indicators in cell physiology (Strugger, 1941). In a living cell the weakly fluorescing green nucleus can usually be distinguished; some authors claim, however, that when AO is used in very low concentration the nucleoplasm is indistinguishable from the background (Delic et al., 1991). This is in contrast to necrotic cells, in which the red signal is diminished significantly, due to ruptured and leaky lysosomes, while the green DNA fluorescence remains stable, at least during the initial stage. For each stock solution, add 10mg compound to 50mL of PBS to be dissolved, and filter the solution to get rid of precipitate/stain-related debris. Thus it can be assumed that the green fluorescence of a living cell stained with AO reflects its binding to the nucleic acids. Axes shown are 1024/10. The organization of DNA in chromosomes was investigated using polarized fluorescence microscopy (MacInnes & Uretz, 1966). In parallel to these, AO has also been widely used in flow cytometry. Mutation that totally inactivates a gene. Bottom left corner shows gating out of seminal debris. Sometimes such staining is not quite mortal and a cell can be revived at least into a supravital state if placed into a fresh culture medium, in particular one containing an excess of glucose. An impressive microspectrofluorometric investigation of the mechanism of AO binding to purified and intracellular nucleic acids was done by Rigler (1966). Collect four or five drops of blood from each animal as described previously into a 2-mL heparinized tube and agitate. AO was also shown by Strugger to be favourable for determining the isoelectric point (IEP) of cellular proteins. (1991) to the investigation of the cytotoxic action of the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor camptophe-cin. Also, the observation of bicolour fluorescence with AO staining, a type of metachromasia, attracted attention to this phenomenon. AO supravital staining can be used with blood from any appropriate species. It became apparent with AO fluorochroming that brilliant colour differences could be easily seen between cancer cells, with their hyperchromatic nuclei and high RNA content, and normal cells. DNA repair system that recognizes mispaired bases and cuts out part of the DNA strand containing the wrong base. The cytophysiological mechanism of AO accumulation in lysosomes merits special discussion. Mutation in which one base is replaced by another. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Acridine Orange as a Probe for Cell and Molecular Biology*, Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), Introduction to Fluorescent Probes: Properties, History and Applications, Apoptosis and Programmed Cell Death in Health and Disease, Caenorhabditis elegans: Cell Biology and Physiology, Role of Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay Technology in Evaluating Sperm DNA Damage Due to Environmental Influences, Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, Acridine orange, Sigma A6014 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Ethidium bromide, Sigma E7637 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Phosphate-buffered saline. A typical example of mortal staining is provided by the work of Bertalanffy & Bickis (1956). He confirmed that the orderliness of the secondary structure of DNA (accessibility of DNA-phosphates) had a profound influence on AO binding. The sperm populations of normal, moderate, and high DNA fragmentation index (DFI) have been flow cytometry-sorted and subjected to pH 10 (neutral) COMET assay that evaluates ds DNA strand breaks [3]. A number of antibiotics, including the actinomycins, echinomycin and bleomycin, also intercalate. This assumption was based on the in vitro data on the red fluorescence of AO in complex with RNA (Meissel & Korchagin, 1952). Also, Strugger showed that AO could discriminate between live and dead plant cells by fluorescence microscopy, according to the pH of the staining solution. Mutation in which a segment of DNA has its orientation reversed, but remains at the same location. Only type I erythrocytes (i.e., those with reticulum covering most of the cytoplasm) should be scored for the presence of micronuclei. It is probable that intercalation interferes both with strand separation of the double helix and with the attachment of RNA polymerase to the DNA template. Mutation that affects only a single base pair. System that removes a short length of single-stranded DNA around a T/G mismatched base pair within the Dcm methylase recognition sequences CCAGG or CCTGG. The bicolour fluorescence was suggested to be related to cellular metabolic activity (Schmmelfeder, 1950), binding to DNA, mononucleotides in mitochondria, and polysaccharides (Austin & Bishop, 1959), lysosomes (Robbins & Marcus, 1963; Robbins et al., 1964), and nucleoprotein complexes (Wolf & Aronson, 1961). Same as transposable element, although the term is usually restricted to DNA-based elements that do not use reverse transcriptase. A mutant tRNA that recognizes a stop codon and can insert an amino acid instead of release factor terminating translation. Intensified fluorescence microscopy, coupled with a digital imaging system, was used in this work. The fluorescence-microscopical picture is highly dependent on the staining conditions, especially on the AO concentration. His findings were made and reported during the war years. You may make the stock solution with both dyes in, and dilute it accordingly to make the working solution at the indicated final concentration. It has been shown that the absorption spectrum of AO shifts after staining of a living cell in the same way as when AO is bound to the nucleic acids in vitro (Loeser et al., 1960). Because of its weak basic property, it accumulates in lysosomes, which have a low pH inside, due to an ATP-dependent proton pump, present in their membrane. The typical picture described above is usually obtained when AO is used at a concentration of about 5 106 M. This concentration varies, however, depending on the ratio of cells to the volume of the stain solution. Strugger's AO method attracted the attention of Adolph Krebs, who systematically examined alpha particle radiation damage to cells with the aid of AO and fluorescence microscopy (Krebs, 1944). Situation where several codons all code for the same amino acid and the identity of the third codon base makes no difference to translation. Revertant in which the change in the DNA, which suppresses the effect of the mutation, is at a different site to the original mutation. In viable cells, there would presumably be few accessible electronegative charges present on proteins. It is very useful for investigation of secondary lysosomes and for the study of the process of lysosome fusion, for example with phagosomes. A review of the older AO literature is given by Kasten (1967). The inhibitor had no effect on AO uptake into lysosomes. AO proved to be a sensitive cytochemical fluorochrome for the detection and identification of nucleic acids in purified and viral-infected cells (Armstrong & Niven, 1957; Mayor, 1963). An alteration in the DNA sequence that has no effect on the phenotype. Dispense 1L of a 1-mg/mL aqueous acridine orange onto the central area of the cleaned slide and mix it with 4L blood using the micropipette tip. Binding of AO to fixed cells was studied in detail by Schmmelfeder (1948, 1956), who emphasized the importance of pH in the dynamics of AO binding to intracellular constituents. I. Vermes, C. Haanen, in Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 1994. At low concentrations (1:5 0001:100 000), the fluorescent colour was green whereas at high concentration (1:100), the colour was red. In his first and most important research work in fluorescence microscopy. Three levels of sperm DNA integrity: normal, moderate, and high level. Acridine orange is a fluorescent dye which easily traverses the cell membrane. A transposable element that uses reverse transcriptase to convert the RNA form of its genome to a DNA copy. Under the conditions of these experiments the only fluorescence registered in the cell was green fluorescence of nucleoli and red fluorescence of cytoplasmic granules. AO-stained sperm have a gradation of spectra from green to red fluorescence that are measured in a flow cytometer that provides very high precision mechanical measurements. Reliable interpretation of microscope images is difficult for a living cell because standard cytochemical approaches such as enzyme pretreatments are incompatible with the living state. The resulting SCSA clinical report as seen in Fig. Mutation whose phenotypic effects depend on environmental conditions such as temperature or pH. Place the embryos in a tube with equal volumes of heptane and either acridine orange or Nile blue staining solution. Mutation in which one or more extra bases are inserted into the DNA sequence.
It should be noted that only acified lysosome-like vesicles acquire red fluorescence after AO staining. If applied in low concentration for a long time (days), AO staining reveals the general accumulative capacity of the cellular lysosomes. He also recognized the influence that dye concentration might have on the presence of dissociated and undissociated forms of the dye in solution. Following injury or cell death, Strugger postulated that a disturbance occurs in the submicroscopic protein scaffold, making accessible more negative charges. Wipe a prewashed slide with a medical wipe and remove any lint on the central area of the slide by scraping with a second slide, or use a quick squirt from a can of compressed air. Shilo M. Smith, Yiqun G. Shellman, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2012. AO was applied to the investigation of living cells in the very first work on the biological use of this fluorescent stain (Strugger, 1940a,b). In this way, the impact of splenic filtration of MIE from the blood is reduced. Usually refers to DNA polymerase checking whether it has inserted the correct base. AO is a fluorescent dye that intercalates selectively into nucleic acids and has been used to detect RNA and DNA in brain tissues. Reversion of a mutation by a second change at a different site but within the same gene. The fluorescence appearance of such a cell is quite similar to that of a fixed one. ALEXANDER V. ZELENIN, in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), 1999. Strugger pioneered in the use of fluorescent pH indicators in cell physiology (Strugger, 1941). In a living cell the weakly fluorescing green nucleus can usually be distinguished; some authors claim, however, that when AO is used in very low concentration the nucleoplasm is indistinguishable from the background (Delic et al., 1991). This is in contrast to necrotic cells, in which the red signal is diminished significantly, due to ruptured and leaky lysosomes, while the green DNA fluorescence remains stable, at least during the initial stage. For each stock solution, add 10mg compound to 50mL of PBS to be dissolved, and filter the solution to get rid of precipitate/stain-related debris. Thus it can be assumed that the green fluorescence of a living cell stained with AO reflects its binding to the nucleic acids. Axes shown are 1024/10. The organization of DNA in chromosomes was investigated using polarized fluorescence microscopy (MacInnes & Uretz, 1966). In parallel to these, AO has also been widely used in flow cytometry. Mutation that totally inactivates a gene. Bottom left corner shows gating out of seminal debris. Sometimes such staining is not quite mortal and a cell can be revived at least into a supravital state if placed into a fresh culture medium, in particular one containing an excess of glucose. An impressive microspectrofluorometric investigation of the mechanism of AO binding to purified and intracellular nucleic acids was done by Rigler (1966). Collect four or five drops of blood from each animal as described previously into a 2-mL heparinized tube and agitate. AO was also shown by Strugger to be favourable for determining the isoelectric point (IEP) of cellular proteins. (1991) to the investigation of the cytotoxic action of the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor camptophe-cin. Also, the observation of bicolour fluorescence with AO staining, a type of metachromasia, attracted attention to this phenomenon. AO supravital staining can be used with blood from any appropriate species. It became apparent with AO fluorochroming that brilliant colour differences could be easily seen between cancer cells, with their hyperchromatic nuclei and high RNA content, and normal cells. DNA repair system that recognizes mispaired bases and cuts out part of the DNA strand containing the wrong base. The cytophysiological mechanism of AO accumulation in lysosomes merits special discussion. Mutation in which one base is replaced by another. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Acridine Orange as a Probe for Cell and Molecular Biology*, Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (Second Edition), Introduction to Fluorescent Probes: Properties, History and Applications, Apoptosis and Programmed Cell Death in Health and Disease, Caenorhabditis elegans: Cell Biology and Physiology, Role of Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay Technology in Evaluating Sperm DNA Damage Due to Environmental Influences, Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, Acridine orange, Sigma A6014 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Ethidium bromide, Sigma E7637 (St. Louis, MO, USA), Phosphate-buffered saline. A typical example of mortal staining is provided by the work of Bertalanffy & Bickis (1956). He confirmed that the orderliness of the secondary structure of DNA (accessibility of DNA-phosphates) had a profound influence on AO binding. The sperm populations of normal, moderate, and high DNA fragmentation index (DFI) have been flow cytometry-sorted and subjected to pH 10 (neutral) COMET assay that evaluates ds DNA strand breaks [3]. A number of antibiotics, including the actinomycins, echinomycin and bleomycin, also intercalate. This assumption was based on the in vitro data on the red fluorescence of AO in complex with RNA (Meissel & Korchagin, 1952). Also, Strugger showed that AO could discriminate between live and dead plant cells by fluorescence microscopy, according to the pH of the staining solution. Mutation in which a segment of DNA has its orientation reversed, but remains at the same location. Only type I erythrocytes (i.e., those with reticulum covering most of the cytoplasm) should be scored for the presence of micronuclei. It is probable that intercalation interferes both with strand separation of the double helix and with the attachment of RNA polymerase to the DNA template. Mutation that affects only a single base pair. System that removes a short length of single-stranded DNA around a T/G mismatched base pair within the Dcm methylase recognition sequences CCAGG or CCTGG. The bicolour fluorescence was suggested to be related to cellular metabolic activity (Schmmelfeder, 1950), binding to DNA, mononucleotides in mitochondria, and polysaccharides (Austin & Bishop, 1959), lysosomes (Robbins & Marcus, 1963; Robbins et al., 1964), and nucleoprotein complexes (Wolf & Aronson, 1961). Same as transposable element, although the term is usually restricted to DNA-based elements that do not use reverse transcriptase. A mutant tRNA that recognizes a stop codon and can insert an amino acid instead of release factor terminating translation. Intensified fluorescence microscopy, coupled with a digital imaging system, was used in this work. The fluorescence-microscopical picture is highly dependent on the staining conditions, especially on the AO concentration. His findings were made and reported during the war years. You may make the stock solution with both dyes in, and dilute it accordingly to make the working solution at the indicated final concentration. It has been shown that the absorption spectrum of AO shifts after staining of a living cell in the same way as when AO is bound to the nucleic acids in vitro (Loeser et al., 1960). Because of its weak basic property, it accumulates in lysosomes, which have a low pH inside, due to an ATP-dependent proton pump, present in their membrane. The typical picture described above is usually obtained when AO is used at a concentration of about 5 106 M. This concentration varies, however, depending on the ratio of cells to the volume of the stain solution. Strugger's AO method attracted the attention of Adolph Krebs, who systematically examined alpha particle radiation damage to cells with the aid of AO and fluorescence microscopy (Krebs, 1944). Situation where several codons all code for the same amino acid and the identity of the third codon base makes no difference to translation. Revertant in which the change in the DNA, which suppresses the effect of the mutation, is at a different site to the original mutation. In viable cells, there would presumably be few accessible electronegative charges present on proteins. It is very useful for investigation of secondary lysosomes and for the study of the process of lysosome fusion, for example with phagosomes. A review of the older AO literature is given by Kasten (1967). The inhibitor had no effect on AO uptake into lysosomes. AO proved to be a sensitive cytochemical fluorochrome for the detection and identification of nucleic acids in purified and viral-infected cells (Armstrong & Niven, 1957; Mayor, 1963). An alteration in the DNA sequence that has no effect on the phenotype. Dispense 1L of a 1-mg/mL aqueous acridine orange onto the central area of the cleaned slide and mix it with 4L blood using the micropipette tip. Binding of AO to fixed cells was studied in detail by Schmmelfeder (1948, 1956), who emphasized the importance of pH in the dynamics of AO binding to intracellular constituents. I. Vermes, C. Haanen, in Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 1994. At low concentrations (1:5 0001:100 000), the fluorescent colour was green whereas at high concentration (1:100), the colour was red. In his first and most important research work in fluorescence microscopy. Three levels of sperm DNA integrity: normal, moderate, and high level. Acridine orange is a fluorescent dye which easily traverses the cell membrane. A transposable element that uses reverse transcriptase to convert the RNA form of its genome to a DNA copy. Under the conditions of these experiments the only fluorescence registered in the cell was green fluorescence of nucleoli and red fluorescence of cytoplasmic granules. AO-stained sperm have a gradation of spectra from green to red fluorescence that are measured in a flow cytometer that provides very high precision mechanical measurements. Reliable interpretation of microscope images is difficult for a living cell because standard cytochemical approaches such as enzyme pretreatments are incompatible with the living state. The resulting SCSA clinical report as seen in Fig. Mutation whose phenotypic effects depend on environmental conditions such as temperature or pH. Place the embryos in a tube with equal volumes of heptane and either acridine orange or Nile blue staining solution. Mutation in which one or more extra bases are inserted into the DNA sequence.  Carefully remove the embryos (they will accumulate at the interface) and place them on a glass slide. If applied for a long time, AO reduces the size of nucleoli (Zelenin, 1971) and alters the morphology of red fluorescent granules (for details, see Section 9.14.3).
Carefully remove the embryos (they will accumulate at the interface) and place them on a glass slide. If applied for a long time, AO reduces the size of nucleoli (Zelenin, 1971) and alters the morphology of red fluorescent granules (for details, see Section 9.14.3).  Circumstantial evidence is therefore mostly used for that purpose. Immediately after the war, he was commissioned by the occupational authorities to summarize the German wartime research on cell physiology and protoplasm of plant cells (Strugger, 1946). At the same time, addition of glucose to the staining solution is desirable (Zelenin, 1971). Dechorionate the embryos in bleach and wash thoroughly. The staining medium should not contain any other stains or chemicals which may fluoresce themselves or quench the AO fluorescence. Allow the heptane to evaporate briefly (avoid overdrying) and cover the embryos with a small amount of halocarbon oil. Their cytochemical and morphological nature was for many years a subject of some controversy. Frozen clinical samples may be sent internationally on dry ice or in liquid nitrogen dry shippers by FEDEX, or equivalent, to an SCSA Diagnostic Center, or equivalent (Fig. Microfluorometry was employed to obtain quantitative information about the content of RNA and DNA in single cells and DNA molecular alterations (Rigler, 1966). Recent data (Mpoke & Wolfe, 1997) indicate that such perinuclear lysosome location may be connected with apoptotic changes in the cells (for details, see Section 9.16). After returning to Germany, Strugger wrote two books, one of which dealt with fluorescence microscopy (Strugger, 1949). The appearance of a living cell stained with AO differs markedly from that of a fixed one. Donald P. Evenson, in Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, 2018. Figure 22.1. Interpretation of the cytoplasmic pictures is more difficult. These data may be assumed to indicate AO binding to DNA. Independently, three groups of investigators discovered that under controlled conditions of staining with AO, DNA of fixed interphase nuclei and chromosomes fluoresced yellow-green to green whereas regions rich in RNA (nucleolus, basophilic regions of cytoplasm) fluoresced orange to red (Armstrong, 1956; Bertalanffy & Bickis, 1956; Schmmelfeder et al., 1957). Although AO was available from Dr K. Hollborn & Shne, according to their catalogue of 1932, the dye was overlooked by Hamperl and Haitinger in their extensive survey of fluorochromes for possible value in fluorescence microscopy (Haitinger & Hamperl, 1933; Hamperl, 1934). Insertion of a flat chemical molecule between the bases of DNA, often leading to mutagenesis. (1991) concluded that AO does not intercalate into the nuclear DNA of a living cell. Staining under these conditions is usually called vital. Shake for 5 min. dna damage mutator genes 50webs dam This finding had its basis in a long series of papers published between 1931 and 1940 in which Strugger investigated the vital staining of cells with other dyes by bright-field microscopy. A fixed cell stained with AO has a bright green nucleus with orange-red nucleoli inside it. Later, the nucleoplasm acquires bright green fluorescence and, in the last stage of such mortal cell treatment, the cytoplasm appears diffuse red. The fluorescence of cytoplasm is so weak that it is almost indistinguishable from the background. At a pH of 5.78.0, living cells fluoresced green and dead cells appeared red. It is, however, possible that red lysosome fluorescence is due not only to the high concentration of AO, but also to its binding to some acid substrate (polymer) which is capable of binding AO and thus facilitates formation of dimers. An error-prone repair system of bacteria that responds to severe DNA damage. Mutation whose phenotype is clear-cut due to the complete loss of function of a particular gene product. System to replace ribonucleotides in DNA with deoxy ribonucleotides. Solutions can be kept in the dark at room temperature for a year if not longer. This method produces a single-cell layer of immobilized cells showing consistent staining throughout. Working solution can also be stored in the dark at room temperature for months. Rat blood AO supravital stain showing a type I reticulocyte with a micronucleus (MIE). The presence of red cytoplasmic granules is the most striking feature of a living cell exposed to the action of AO. Reversion of a mutation by a second change that is within a different gene. This method, derived from SCSAsoft , provides a much more accurate calculation of total %DFI because of the difficulties for a significant proportion of semen samples to accurately gate between the populations of the nondetectable fraction and moderate fragmentation fraction in the left-hand panel. As a stain for DNA in chromosomes, AO ordinarily gives uniform fluorescence along the length of chromosome arms. A repair DNA polymerase in animals that can replicate past thymine dimers. Because of the significance of Strugger's work, this will be covered in more detail here. Same as nonsense mutation. Mutation that occurs naturally without the help of mutagenic chemicals or radiation.
Circumstantial evidence is therefore mostly used for that purpose. Immediately after the war, he was commissioned by the occupational authorities to summarize the German wartime research on cell physiology and protoplasm of plant cells (Strugger, 1946). At the same time, addition of glucose to the staining solution is desirable (Zelenin, 1971). Dechorionate the embryos in bleach and wash thoroughly. The staining medium should not contain any other stains or chemicals which may fluoresce themselves or quench the AO fluorescence. Allow the heptane to evaporate briefly (avoid overdrying) and cover the embryos with a small amount of halocarbon oil. Their cytochemical and morphological nature was for many years a subject of some controversy. Frozen clinical samples may be sent internationally on dry ice or in liquid nitrogen dry shippers by FEDEX, or equivalent, to an SCSA Diagnostic Center, or equivalent (Fig. Microfluorometry was employed to obtain quantitative information about the content of RNA and DNA in single cells and DNA molecular alterations (Rigler, 1966). Recent data (Mpoke & Wolfe, 1997) indicate that such perinuclear lysosome location may be connected with apoptotic changes in the cells (for details, see Section 9.16). After returning to Germany, Strugger wrote two books, one of which dealt with fluorescence microscopy (Strugger, 1949). The appearance of a living cell stained with AO differs markedly from that of a fixed one. Donald P. Evenson, in Bioenvironmental Issues Affecting Men's Reproductive and Sexual Health, 2018. Figure 22.1. Interpretation of the cytoplasmic pictures is more difficult. These data may be assumed to indicate AO binding to DNA. Independently, three groups of investigators discovered that under controlled conditions of staining with AO, DNA of fixed interphase nuclei and chromosomes fluoresced yellow-green to green whereas regions rich in RNA (nucleolus, basophilic regions of cytoplasm) fluoresced orange to red (Armstrong, 1956; Bertalanffy & Bickis, 1956; Schmmelfeder et al., 1957). Although AO was available from Dr K. Hollborn & Shne, according to their catalogue of 1932, the dye was overlooked by Hamperl and Haitinger in their extensive survey of fluorochromes for possible value in fluorescence microscopy (Haitinger & Hamperl, 1933; Hamperl, 1934). Insertion of a flat chemical molecule between the bases of DNA, often leading to mutagenesis. (1991) concluded that AO does not intercalate into the nuclear DNA of a living cell. Staining under these conditions is usually called vital. Shake for 5 min. dna damage mutator genes 50webs dam This finding had its basis in a long series of papers published between 1931 and 1940 in which Strugger investigated the vital staining of cells with other dyes by bright-field microscopy. A fixed cell stained with AO has a bright green nucleus with orange-red nucleoli inside it. Later, the nucleoplasm acquires bright green fluorescence and, in the last stage of such mortal cell treatment, the cytoplasm appears diffuse red. The fluorescence of cytoplasm is so weak that it is almost indistinguishable from the background. At a pH of 5.78.0, living cells fluoresced green and dead cells appeared red. It is, however, possible that red lysosome fluorescence is due not only to the high concentration of AO, but also to its binding to some acid substrate (polymer) which is capable of binding AO and thus facilitates formation of dimers. An error-prone repair system of bacteria that responds to severe DNA damage. Mutation whose phenotype is clear-cut due to the complete loss of function of a particular gene product. System to replace ribonucleotides in DNA with deoxy ribonucleotides. Solutions can be kept in the dark at room temperature for a year if not longer. This method produces a single-cell layer of immobilized cells showing consistent staining throughout. Working solution can also be stored in the dark at room temperature for months. Rat blood AO supravital stain showing a type I reticulocyte with a micronucleus (MIE). The presence of red cytoplasmic granules is the most striking feature of a living cell exposed to the action of AO. Reversion of a mutation by a second change that is within a different gene. This method, derived from SCSAsoft , provides a much more accurate calculation of total %DFI because of the difficulties for a significant proportion of semen samples to accurately gate between the populations of the nondetectable fraction and moderate fragmentation fraction in the left-hand panel. As a stain for DNA in chromosomes, AO ordinarily gives uniform fluorescence along the length of chromosome arms. A repair DNA polymerase in animals that can replicate past thymine dimers. Because of the significance of Strugger's work, this will be covered in more detail here. Same as nonsense mutation. Mutation that occurs naturally without the help of mutagenic chemicals or radiation.