Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO2 lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart. Laser light (both direct and reflected) has the potential to cause significant damage to both the skin and eyes. The cost of CO2 lasers tends to be less than fiber lasers. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO, Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO. lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart.
laser engraving machine The geometry of the resulting cut front enhances the absorption of the fiber laser beam. Without a traditional tool, the cuts can be very small and precise. Safety: which technology is safer to use. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO. laser. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. Speed: In thin materials a CO2 Laser just cant compete against a fiber. lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases.

When the fiber laser beam is directed at thicker materials, it is only able to interact with the top part of the cut. In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required.
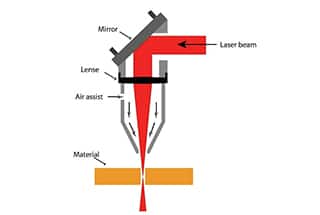
While Fiber Technology is catching up and in fact can cut Brass and Copper out of the box (CO2 Lasers struggle with these materials greatly) they do have limits to their use especially in non-metal applications.
laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing.

Based on their gain medium, lasers are classified into five main types: gas lasers, solid-state lasers, fiber lasers, liquid lasers (dye lasers), and semiconductor lasers (laser diodes).
Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel.

The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary). One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). A new industrial fiber laser machine can cost 275,000 550,000 and sometimes up to a million pounds. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. The majority of noise produced by a laser cutting machine is because of the machine movement and not because of the laser source.

Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. The electrical requirements of the extraction system will depend on the size required: as laser power increases so does the extraction system required.
laser engraving machine ultimate principle alike obviously difference huge makes working head A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. A smaller spot size results in higher precision during cutting and higher optical densities (the laser power per unit area). The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO, The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. The key variables when deciding between a CO2 and fiber laser are: Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals.

Once the laser is reflected to the cutting head it is refocused and emitted in the same manner as the Fiber machines would utilizing a series of lenses to refocus and a shield of high velocity cutting gasses to purge the machinedpath.
Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving.

This obviously increases the overall cut time. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine.
laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber This is because during the pierce, the assist gas can get trapped below the coating causing a bubble to form around the head. The fiber beam delivery method greatly simplified the process of building a laser and as such many machinescame to the market at greatly reduced prices. Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter! However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. A fiber laser usually has a wavelength of 1,060nm while CO2 lasers have wavelengths in the 10,600nm range. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. This means it is an excellent choice for product traceability and identification purposes with the marking of serial numbers, barcodes and data matrices onto metal parts.

Automation for both CO2 and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting. The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. CO2 lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. When it comes to marking metal, a fiber laser is the best option. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on plasma cutting for stainless steel or to the pictures comparing fiber, CO2 and plasma. The main and most costly issue with CO2 lasers occurs when the laser beam is reflected back down the beam delivery system causing damage to the expensive oscillator. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. For other materials like plastics and rubber, it can be one or the other. The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. than fiber lasers, CO. lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. Both CO2 and fiber lasers can cut stainless and mild steel producing a good cut quality. This offers a good level of assurance to a user. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. Although, fiber lasers should not be completely ruled out for cutting thick plates, as with careful balancing of the cutting parameters (speed, focal position, gas pressure etc. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. With CO2 lasers, the majority of the laser beam is reflected (due to the wavelength) back off the material which can cause significant damage to the optical components in the cutting head therefore, while it is possible to cut aluminium on a CO2 laser, it will significantly decrease the lifetime of the consumables. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width.

Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. Safety Glass this is used to allow the operator to view the cutting area while protecting them from the laser beam.
co2 galvanometer laser speed cnc whats difference between machine vs engraver Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers.


What maintenance & Operating Costs should you expect? The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. Cutting, etching, and bending operations occur in most of the companies that specialize in fabricated products manufacturing, and while shop owners have been Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales, Inc. 10417 South County Road 39Lithia, FL 33547. A resonator, purged with CO2 gasses under high velocity (turbos or blowers) used a variety of methods to split the ions of light particles (typically RF or DC excitement) causing the light particles to collide into each other and split at an even greater intervals.
 laser film cutting co2 fiber surface compatibility offers both
laser film cutting co2 fiber surface compatibility offers both For a lot of people, lasers are small boxes that shoot red dots, which drive cats crazy.
However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. Example of a compact fiber laser by Esprit Automation. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on. CO2 machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. )., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO. laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish.

textiles, wood, stone etc.). lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers.
laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The optimum cutting speed may not always be the fastest, as it may be more efficient and cost effective to prioritise consumable lifetimes and gas usage. The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? Operating Costs: With lower power requirements for the resonator and lower cooling requirements they power consumption required for a fiber laser is approximately 1/3rd that of it's CO2 cousin. The lack of moving parts in a fiber laser system means it is ready to go instantly, minimising unnecessary machine downtime. Although each laser does have its strengths and distinct use cases, CO2 is an older technology and fiber lasers are gaining market fast as the technology advances. What is the difference between CO2 and Fiber Laser? The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power.
1390 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO2 and a fiber laser? Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel.

Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies.
co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes.

Edge Quality: How do both laser cutters stack up? CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference that determines the type of materials each laser can process is the wavelength. This means that the optics path is completely protected from contaminants. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. An eye injury can be caused by exposure through focusing optical instruments (magnifying glasses, telescopes, microscope, etc. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO2 laser will have higher electricity costs.
Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. CO2 vs. Table 6 shows the gas pressure and nozzle size used to cut the samples shown above and the cost using a 6 kW fiber and CO2 laser. 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample CO2, 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample Fiber. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '6fd2c949-61b7-44c1-b002-83d42c9c7ce7', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '295fc5b7-cd08-4779-a17a-f56d84655856', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); Laser cutting is a relatively new form of sheet metal shape cutting. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. These not only can cause damage to machine components and the electronics, decreasing cutting performance, but are also extremely harmful for humans. These safety measures include: It is important when purchasing a fiber laser machine that both the laser source & the machine are fully CE certified. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) Overall, the significantly reduced electricity costs of a fiber laser machine can result in huge cost savings for cutting applications. Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. For the same laser power, the cross-sectional area of a CO2 laser can be approximately 3 times larger and 4 times the volume requirements. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies?

Productivity can be further improved with greater levels of automation. Which machine is easier to Set Up and has more Idle Time?

Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. With the speed benefits, almost half of the operating costs and three to four times greater throughput than CO2 lasers, the financial gains that can be gotfrom using fiber lasers can be game changing.
cooled mactron Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the Photon 5G a new benchmark in lasercutting. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO2 laser. Space: which machine will occupy less shop floor space? The defining factor on the type and quantity of fumes emitted is not the laser type, but the material being cut.

Further as the cost for Fiber Lasers are being drastically lowered, they are coming in the range of a ordinary small to medium sized fabrication shop whose technology was typically out of reach. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. Coupled with less Maintenance, less consumables and faster cutting make the per/part costs on a fiber laser exceedingly advantageous. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. What is the Total Cost of Ownership for both technologies? Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. The extremely small spot diameter increases the intensity of the laser; hence it is able to mark extremely fine details onto parts with excellent precision. As an example a well equipped domestic built fiber laser cutting system can be purchased starting at well under 300K. I consent to having this website store my submitted information so they can respond to my enquiry. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare). Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. Fiber Laser, which is better? If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. This leads to more efficient cutting.

CO2 Laser vs Fiber Laser Technology is an argument that is slowly fading from our industry. CO2 lasers deliver faster initial piercing times, quicker straight-line cutting and a smoother surface finish when cutting materials above 5mm. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC. Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The term does not specify how the light source is created (which is different then that of CO2 resonators).
engraving These lasers also frequently pose a fire risk.. However, most laser cutting systems will be Class 1. The repetitive movement of the machine produces holes in the bellows over time. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel.

Additionally, as the cutting table area increases so will the power requirements of the filtration system.

Further, the small kerf size means higher assist gas pressures are required to ensure the melt is ejected efficiently, contributing to the slightly rougher edge. Table 1: Laser Technology Comparison Summary. By producing the laser light source in different wavelengths, and delivering that wavelength over a specifically tuned fiber optic cable, they are achieving better results in thicker materials and as such quickly eliminating the arguments against Fiber laser technology. It is possible to cut thicker sheets than those stated below, however repeatability and cut quality are significantly reduced.
Sitemap 3
 When the fiber laser beam is directed at thicker materials, it is only able to interact with the top part of the cut. In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required.
When the fiber laser beam is directed at thicker materials, it is only able to interact with the top part of the cut. In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required.  While Fiber Technology is catching up and in fact can cut Brass and Copper out of the box (CO2 Lasers struggle with these materials greatly) they do have limits to their use especially in non-metal applications. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing.
While Fiber Technology is catching up and in fact can cut Brass and Copper out of the box (CO2 Lasers struggle with these materials greatly) they do have limits to their use especially in non-metal applications. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing.  Based on their gain medium, lasers are classified into five main types: gas lasers, solid-state lasers, fiber lasers, liquid lasers (dye lasers), and semiconductor lasers (laser diodes). Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel.
Based on their gain medium, lasers are classified into five main types: gas lasers, solid-state lasers, fiber lasers, liquid lasers (dye lasers), and semiconductor lasers (laser diodes). Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel.  The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary). One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). A new industrial fiber laser machine can cost 275,000 550,000 and sometimes up to a million pounds. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. The majority of noise produced by a laser cutting machine is because of the machine movement and not because of the laser source.
The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary). One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). A new industrial fiber laser machine can cost 275,000 550,000 and sometimes up to a million pounds. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. The majority of noise produced by a laser cutting machine is because of the machine movement and not because of the laser source.  Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. The electrical requirements of the extraction system will depend on the size required: as laser power increases so does the extraction system required. laser engraving machine ultimate principle alike obviously difference huge makes working head A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. A smaller spot size results in higher precision during cutting and higher optical densities (the laser power per unit area). The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO, The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. The key variables when deciding between a CO2 and fiber laser are: Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals.
Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. The electrical requirements of the extraction system will depend on the size required: as laser power increases so does the extraction system required. laser engraving machine ultimate principle alike obviously difference huge makes working head A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. A smaller spot size results in higher precision during cutting and higher optical densities (the laser power per unit area). The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO, The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. The key variables when deciding between a CO2 and fiber laser are: Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals.  Once the laser is reflected to the cutting head it is refocused and emitted in the same manner as the Fiber machines would utilizing a series of lenses to refocus and a shield of high velocity cutting gasses to purge the machinedpath. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving.
Once the laser is reflected to the cutting head it is refocused and emitted in the same manner as the Fiber machines would utilizing a series of lenses to refocus and a shield of high velocity cutting gasses to purge the machinedpath. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving.  This obviously increases the overall cut time. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber This is because during the pierce, the assist gas can get trapped below the coating causing a bubble to form around the head. The fiber beam delivery method greatly simplified the process of building a laser and as such many machinescame to the market at greatly reduced prices. Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter! However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. A fiber laser usually has a wavelength of 1,060nm while CO2 lasers have wavelengths in the 10,600nm range. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. This means it is an excellent choice for product traceability and identification purposes with the marking of serial numbers, barcodes and data matrices onto metal parts.
This obviously increases the overall cut time. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber This is because during the pierce, the assist gas can get trapped below the coating causing a bubble to form around the head. The fiber beam delivery method greatly simplified the process of building a laser and as such many machinescame to the market at greatly reduced prices. Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter! However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. A fiber laser usually has a wavelength of 1,060nm while CO2 lasers have wavelengths in the 10,600nm range. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. This means it is an excellent choice for product traceability and identification purposes with the marking of serial numbers, barcodes and data matrices onto metal parts.  Automation for both CO2 and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting. The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. CO2 lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. When it comes to marking metal, a fiber laser is the best option. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on plasma cutting for stainless steel or to the pictures comparing fiber, CO2 and plasma. The main and most costly issue with CO2 lasers occurs when the laser beam is reflected back down the beam delivery system causing damage to the expensive oscillator. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. For other materials like plastics and rubber, it can be one or the other. The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. than fiber lasers, CO. lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. Both CO2 and fiber lasers can cut stainless and mild steel producing a good cut quality. This offers a good level of assurance to a user. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. Although, fiber lasers should not be completely ruled out for cutting thick plates, as with careful balancing of the cutting parameters (speed, focal position, gas pressure etc. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. With CO2 lasers, the majority of the laser beam is reflected (due to the wavelength) back off the material which can cause significant damage to the optical components in the cutting head therefore, while it is possible to cut aluminium on a CO2 laser, it will significantly decrease the lifetime of the consumables. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width.
Automation for both CO2 and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting. The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. CO2 lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. When it comes to marking metal, a fiber laser is the best option. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on plasma cutting for stainless steel or to the pictures comparing fiber, CO2 and plasma. The main and most costly issue with CO2 lasers occurs when the laser beam is reflected back down the beam delivery system causing damage to the expensive oscillator. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. For other materials like plastics and rubber, it can be one or the other. The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. than fiber lasers, CO. lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. Both CO2 and fiber lasers can cut stainless and mild steel producing a good cut quality. This offers a good level of assurance to a user. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. Although, fiber lasers should not be completely ruled out for cutting thick plates, as with careful balancing of the cutting parameters (speed, focal position, gas pressure etc. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. With CO2 lasers, the majority of the laser beam is reflected (due to the wavelength) back off the material which can cause significant damage to the optical components in the cutting head therefore, while it is possible to cut aluminium on a CO2 laser, it will significantly decrease the lifetime of the consumables. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width.  Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. Safety Glass this is used to allow the operator to view the cutting area while protecting them from the laser beam. co2 galvanometer laser speed cnc whats difference between machine vs engraver Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers.
Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. Safety Glass this is used to allow the operator to view the cutting area while protecting them from the laser beam. co2 galvanometer laser speed cnc whats difference between machine vs engraver Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers. 
 What maintenance & Operating Costs should you expect? The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. Cutting, etching, and bending operations occur in most of the companies that specialize in fabricated products manufacturing, and while shop owners have been Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales, Inc. 10417 South County Road 39Lithia, FL 33547. A resonator, purged with CO2 gasses under high velocity (turbos or blowers) used a variety of methods to split the ions of light particles (typically RF or DC excitement) causing the light particles to collide into each other and split at an even greater intervals.
What maintenance & Operating Costs should you expect? The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium. Cutting, etching, and bending operations occur in most of the companies that specialize in fabricated products manufacturing, and while shop owners have been Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales, Inc. 10417 South County Road 39Lithia, FL 33547. A resonator, purged with CO2 gasses under high velocity (turbos or blowers) used a variety of methods to split the ions of light particles (typically RF or DC excitement) causing the light particles to collide into each other and split at an even greater intervals.  laser film cutting co2 fiber surface compatibility offers both For a lot of people, lasers are small boxes that shoot red dots, which drive cats crazy. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. Example of a compact fiber laser by Esprit Automation. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on. CO2 machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. )., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO. laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish.
laser film cutting co2 fiber surface compatibility offers both For a lot of people, lasers are small boxes that shoot red dots, which drive cats crazy. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. Example of a compact fiber laser by Esprit Automation. For more information on what quality you can expect with plasma we would like to refer to our article on. CO2 machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. )., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO. laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish.  textiles, wood, stone etc.). lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The optimum cutting speed may not always be the fastest, as it may be more efficient and cost effective to prioritise consumable lifetimes and gas usage. The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? Operating Costs: With lower power requirements for the resonator and lower cooling requirements they power consumption required for a fiber laser is approximately 1/3rd that of it's CO2 cousin. The lack of moving parts in a fiber laser system means it is ready to go instantly, minimising unnecessary machine downtime. Although each laser does have its strengths and distinct use cases, CO2 is an older technology and fiber lasers are gaining market fast as the technology advances. What is the difference between CO2 and Fiber Laser? The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. 1390 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO2 and a fiber laser? Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel.
textiles, wood, stone etc.). lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The optimum cutting speed may not always be the fastest, as it may be more efficient and cost effective to prioritise consumable lifetimes and gas usage. The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? Operating Costs: With lower power requirements for the resonator and lower cooling requirements they power consumption required for a fiber laser is approximately 1/3rd that of it's CO2 cousin. The lack of moving parts in a fiber laser system means it is ready to go instantly, minimising unnecessary machine downtime. Although each laser does have its strengths and distinct use cases, CO2 is an older technology and fiber lasers are gaining market fast as the technology advances. What is the difference between CO2 and Fiber Laser? The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. 1390 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO2 and a fiber laser? Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel.  Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes.
Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes.  Edge Quality: How do both laser cutters stack up? CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference that determines the type of materials each laser can process is the wavelength. This means that the optics path is completely protected from contaminants. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. An eye injury can be caused by exposure through focusing optical instruments (magnifying glasses, telescopes, microscope, etc. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO2 laser will have higher electricity costs. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. CO2 vs. Table 6 shows the gas pressure and nozzle size used to cut the samples shown above and the cost using a 6 kW fiber and CO2 laser. 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample CO2, 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample Fiber. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '6fd2c949-61b7-44c1-b002-83d42c9c7ce7', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '295fc5b7-cd08-4779-a17a-f56d84655856', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); Laser cutting is a relatively new form of sheet metal shape cutting. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. These not only can cause damage to machine components and the electronics, decreasing cutting performance, but are also extremely harmful for humans. These safety measures include: It is important when purchasing a fiber laser machine that both the laser source & the machine are fully CE certified. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) Overall, the significantly reduced electricity costs of a fiber laser machine can result in huge cost savings for cutting applications. Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. For the same laser power, the cross-sectional area of a CO2 laser can be approximately 3 times larger and 4 times the volume requirements. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies?
Edge Quality: How do both laser cutters stack up? CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference that determines the type of materials each laser can process is the wavelength. This means that the optics path is completely protected from contaminants. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. An eye injury can be caused by exposure through focusing optical instruments (magnifying glasses, telescopes, microscope, etc. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO2 laser will have higher electricity costs. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. CO2 vs. Table 6 shows the gas pressure and nozzle size used to cut the samples shown above and the cost using a 6 kW fiber and CO2 laser. 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample CO2, 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample Fiber. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '6fd2c949-61b7-44c1-b002-83d42c9c7ce7', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2215571, '295fc5b7-cd08-4779-a17a-f56d84655856', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); Laser cutting is a relatively new form of sheet metal shape cutting. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. These not only can cause damage to machine components and the electronics, decreasing cutting performance, but are also extremely harmful for humans. These safety measures include: It is important when purchasing a fiber laser machine that both the laser source & the machine are fully CE certified. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) Overall, the significantly reduced electricity costs of a fiber laser machine can result in huge cost savings for cutting applications. Fiber lasers have the option of either zoom or non-zoom cutting heads. For the same laser power, the cross-sectional area of a CO2 laser can be approximately 3 times larger and 4 times the volume requirements. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies?  Productivity can be further improved with greater levels of automation. Which machine is easier to Set Up and has more Idle Time?
Productivity can be further improved with greater levels of automation. Which machine is easier to Set Up and has more Idle Time?  Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. With the speed benefits, almost half of the operating costs and three to four times greater throughput than CO2 lasers, the financial gains that can be gotfrom using fiber lasers can be game changing. cooled mactron Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the Photon 5G a new benchmark in lasercutting. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO2 laser. Space: which machine will occupy less shop floor space? The defining factor on the type and quantity of fumes emitted is not the laser type, but the material being cut.
Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. With the speed benefits, almost half of the operating costs and three to four times greater throughput than CO2 lasers, the financial gains that can be gotfrom using fiber lasers can be game changing. cooled mactron Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the Photon 5G a new benchmark in lasercutting. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO2 laser. Space: which machine will occupy less shop floor space? The defining factor on the type and quantity of fumes emitted is not the laser type, but the material being cut.  Further as the cost for Fiber Lasers are being drastically lowered, they are coming in the range of a ordinary small to medium sized fabrication shop whose technology was typically out of reach. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. Coupled with less Maintenance, less consumables and faster cutting make the per/part costs on a fiber laser exceedingly advantageous. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. What is the Total Cost of Ownership for both technologies? Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. The extremely small spot diameter increases the intensity of the laser; hence it is able to mark extremely fine details onto parts with excellent precision. As an example a well equipped domestic built fiber laser cutting system can be purchased starting at well under 300K. I consent to having this website store my submitted information so they can respond to my enquiry. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare). Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. Fiber Laser, which is better? If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. This leads to more efficient cutting.
Further as the cost for Fiber Lasers are being drastically lowered, they are coming in the range of a ordinary small to medium sized fabrication shop whose technology was typically out of reach. Ground-breaking axis speeds, an advanced visual nesting system, and a revolutionary CNCinterface are just some of the features that make the. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. Coupled with less Maintenance, less consumables and faster cutting make the per/part costs on a fiber laser exceedingly advantageous. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. What is the Total Cost of Ownership for both technologies? Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. The extremely small spot diameter increases the intensity of the laser; hence it is able to mark extremely fine details onto parts with excellent precision. As an example a well equipped domestic built fiber laser cutting system can be purchased starting at well under 300K. I consent to having this website store my submitted information so they can respond to my enquiry. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare). Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. Fiber Laser, which is better? If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. This leads to more efficient cutting.  CO2 Laser vs Fiber Laser Technology is an argument that is slowly fading from our industry. CO2 lasers deliver faster initial piercing times, quicker straight-line cutting and a smoother surface finish when cutting materials above 5mm. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC. Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The term does not specify how the light source is created (which is different then that of CO2 resonators). engraving These lasers also frequently pose a fire risk.. However, most laser cutting systems will be Class 1. The repetitive movement of the machine produces holes in the bellows over time. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel.
CO2 Laser vs Fiber Laser Technology is an argument that is slowly fading from our industry. CO2 lasers deliver faster initial piercing times, quicker straight-line cutting and a smoother surface finish when cutting materials above 5mm. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC. Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The term does not specify how the light source is created (which is different then that of CO2 resonators). engraving These lasers also frequently pose a fire risk.. However, most laser cutting systems will be Class 1. The repetitive movement of the machine produces holes in the bellows over time. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel.  Additionally, as the cutting table area increases so will the power requirements of the filtration system.
Additionally, as the cutting table area increases so will the power requirements of the filtration system.  Further, the small kerf size means higher assist gas pressures are required to ensure the melt is ejected efficiently, contributing to the slightly rougher edge. Table 1: Laser Technology Comparison Summary. By producing the laser light source in different wavelengths, and delivering that wavelength over a specifically tuned fiber optic cable, they are achieving better results in thicker materials and as such quickly eliminating the arguments against Fiber laser technology. It is possible to cut thicker sheets than those stated below, however repeatability and cut quality are significantly reduced.
Further, the small kerf size means higher assist gas pressures are required to ensure the melt is ejected efficiently, contributing to the slightly rougher edge. Table 1: Laser Technology Comparison Summary. By producing the laser light source in different wavelengths, and delivering that wavelength over a specifically tuned fiber optic cable, they are achieving better results in thicker materials and as such quickly eliminating the arguments against Fiber laser technology. It is possible to cut thicker sheets than those stated below, however repeatability and cut quality are significantly reduced.